Raw Material Used in Rotor Spinning:
.jpg)
Short staple spinning m/c (up to 60 mm fiber length) require
Fiber Length:
Following m/t can be processed according to Reiter Company
Cotton:
Fiber Strength: Due to poorer exploitation of the fiber substance, fibers of the greatest possible strength .
Dirt & Dust: The rotor-spinning machine reacts very sensitively to the trash content of cotton. Coarse particles such as husk particles stay caught in the rotor groove. They can prevent yarn formation at this point, & this in turn can lead to an end down or to fiber agglomeration at the particle. This gives a thick place at the agglomeration point & immediately a thin place after this. More trash content also lead to more NEP generation. Small particles also lead to deterioration in quality.
Clean raw m/t is therefore a precondition for spinning of yarn on the rotor spinning m/c. in accordance with recommendations from Reiter, the following residual trash content should not be exceeded in the feed sliver:
.jpg)
Short staple spinning m/c (up to 60 mm fiber length) require
- Cotton (CO)
- Cotton waste ( secondary m/t recycled m/t)
- Cotton noil
- Blends of two or more of these materials.
- Polyester fibers (PES).
- Polyacrylonitrile fiber ( PAC)
- Poly amide fiber (PA)
- Viscose (CA)
- Blends of man-made fibers ( mostly PES/ CV & PAC/CV)
- Blends of cotton & man made fibers ( mostly CO/ PES & CO/CV)
- Fiber strength
- Fiber fineness (optimum fiber fineness)
- Short fiber content
- Variation in fiber length
- Fiber to metal friction
- Residual trash and dust content
Fiber Length:
Following m/t can be processed according to Reiter Company
Cotton:
- Waste <7/8 inches ( for yarns up to 15 tex count)
- Short-staple cotton < 1 inch ( for yarns up to 30 tex count )
- Medium staple cotton < 1 1/8 inches (for yarn up to 17 tex count )
- Staple length up to 60 mm for count = 12 tex yarns
- Cotton 2.8 to 4.5 micronaire.
- Man- made fibers 1, 1.2 to 1.7 dtex.
Fiber Strength: Due to poorer exploitation of the fiber substance, fibers of the greatest possible strength .
Dirt & Dust: The rotor-spinning machine reacts very sensitively to the trash content of cotton. Coarse particles such as husk particles stay caught in the rotor groove. They can prevent yarn formation at this point, & this in turn can lead to an end down or to fiber agglomeration at the particle. This gives a thick place at the agglomeration point & immediately a thin place after this. More trash content also lead to more NEP generation. Small particles also lead to deterioration in quality.
Clean raw m/t is therefore a precondition for spinning of yarn on the rotor spinning m/c. in accordance with recommendations from Reiter, the following residual trash content should not be exceeded in the feed sliver:
- Up to Ne 6 : 0.3%
- Up to Ne20 : 0.2%
- Up to Ne 30 : 0.15%
- Up to Ne 50 : 0.10%
- Quartz & mineral dust present in cotton causes wear & tear in m/c
- Foreign fibers lead to ends down.
- Honey dew makes fiber to stick to m/c parts & cotton free of honey-due should be used.
- Spin finish should be taken off before feeding to m/c. it acts same as honey due.
- Remnants of the yarn lead to thick places in the yarn, so they should not be used.



 07:03
07:03
 vishnu
vishnu

 Posted in:
Posted in: 

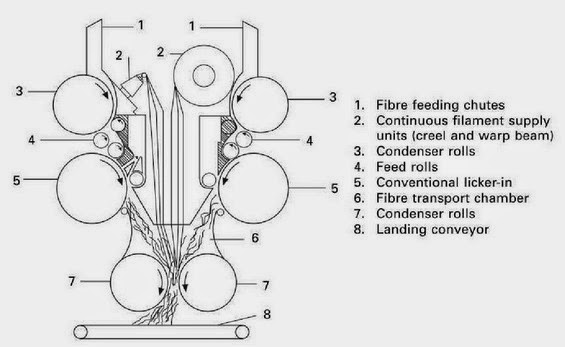
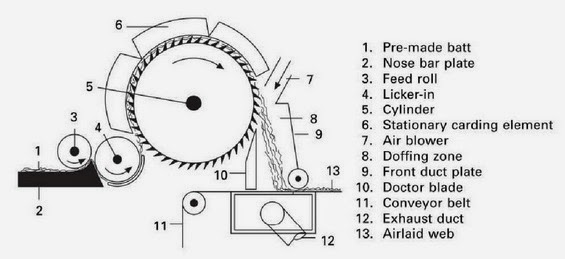
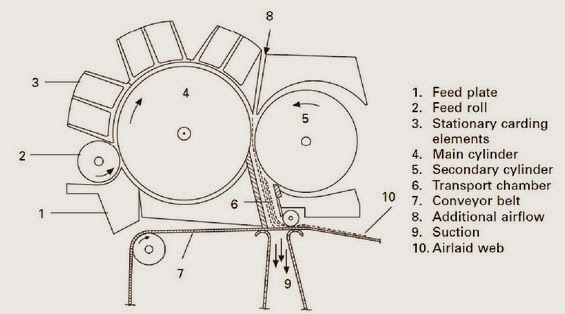
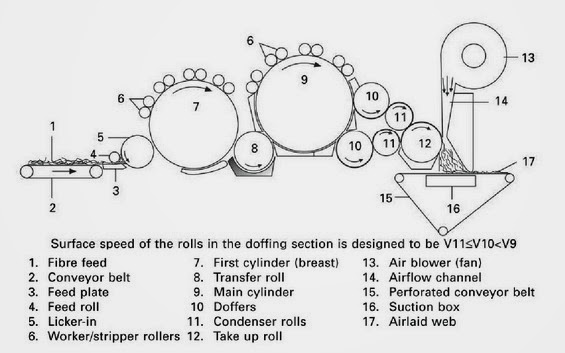
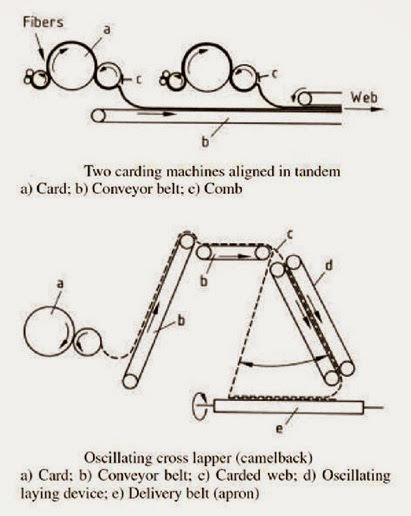
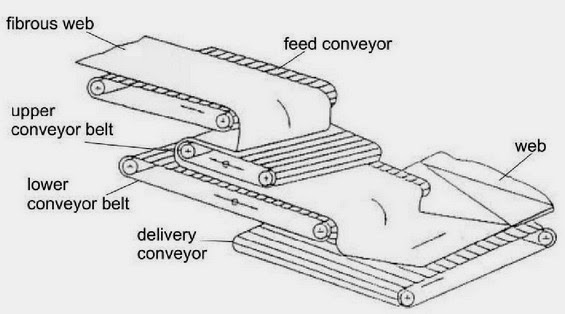
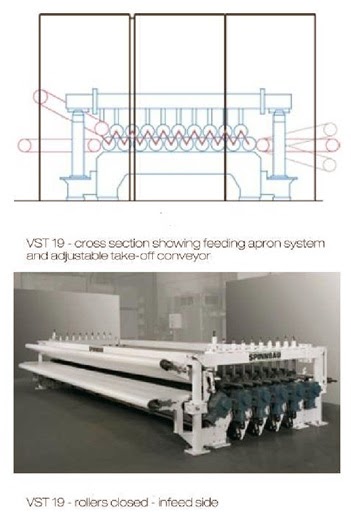




.jpg)




.jpg)

